Benchmarking (Internal)
This page documents the internal benchmarking tools used for performance testing py-draughts.
Performance Results
The following benchmarks were run on January 7, 2026.
Legal Moves Generation
Performance of the legal moves generator across different board positions:
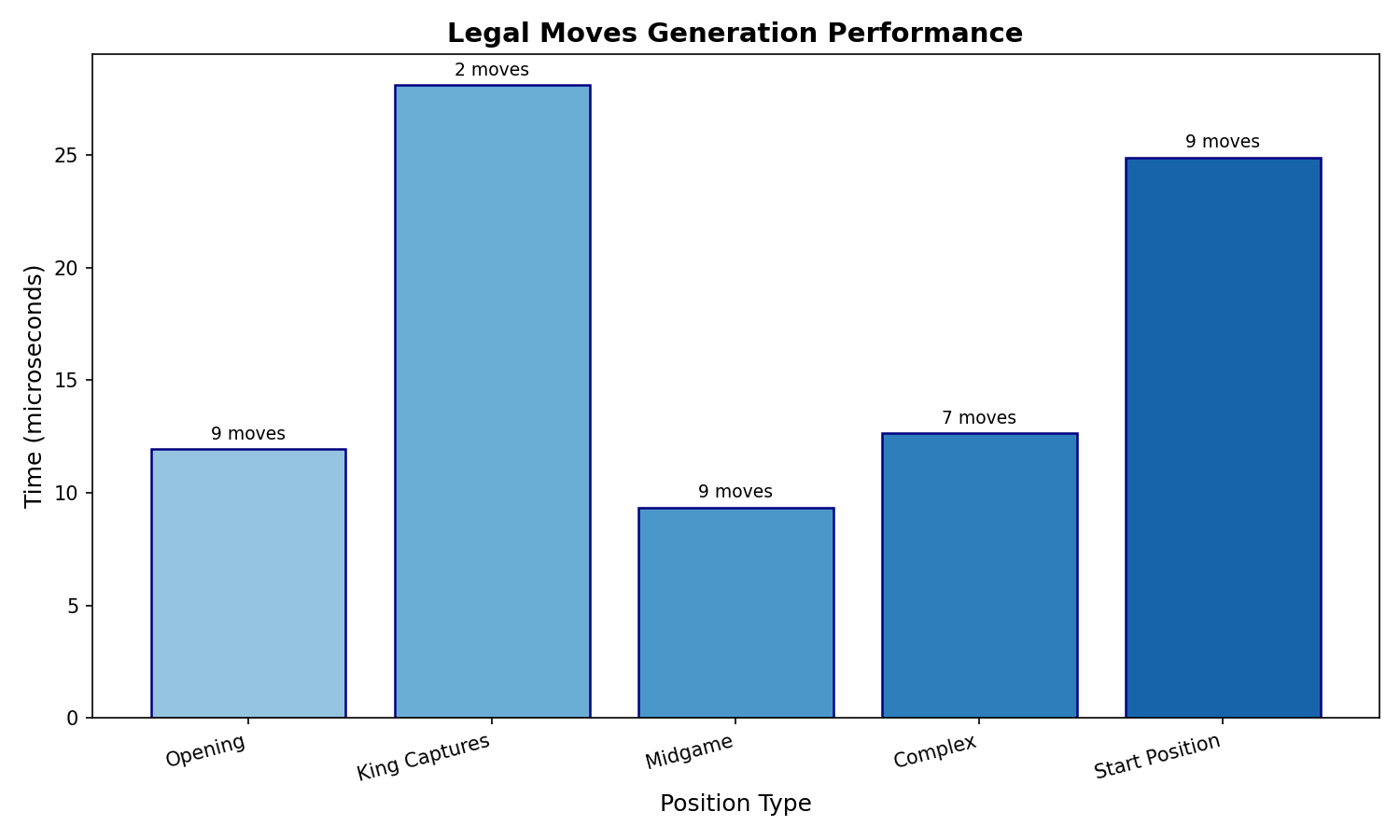
Position Type |
Time (µs) |
Move Count |
|---|---|---|
Opening |
11.93 |
9 |
King Captures |
28.10 |
2 |
Midgame |
9.36 |
9 |
Complex |
12.64 |
7 |
Start Position |
24.90 |
9 |
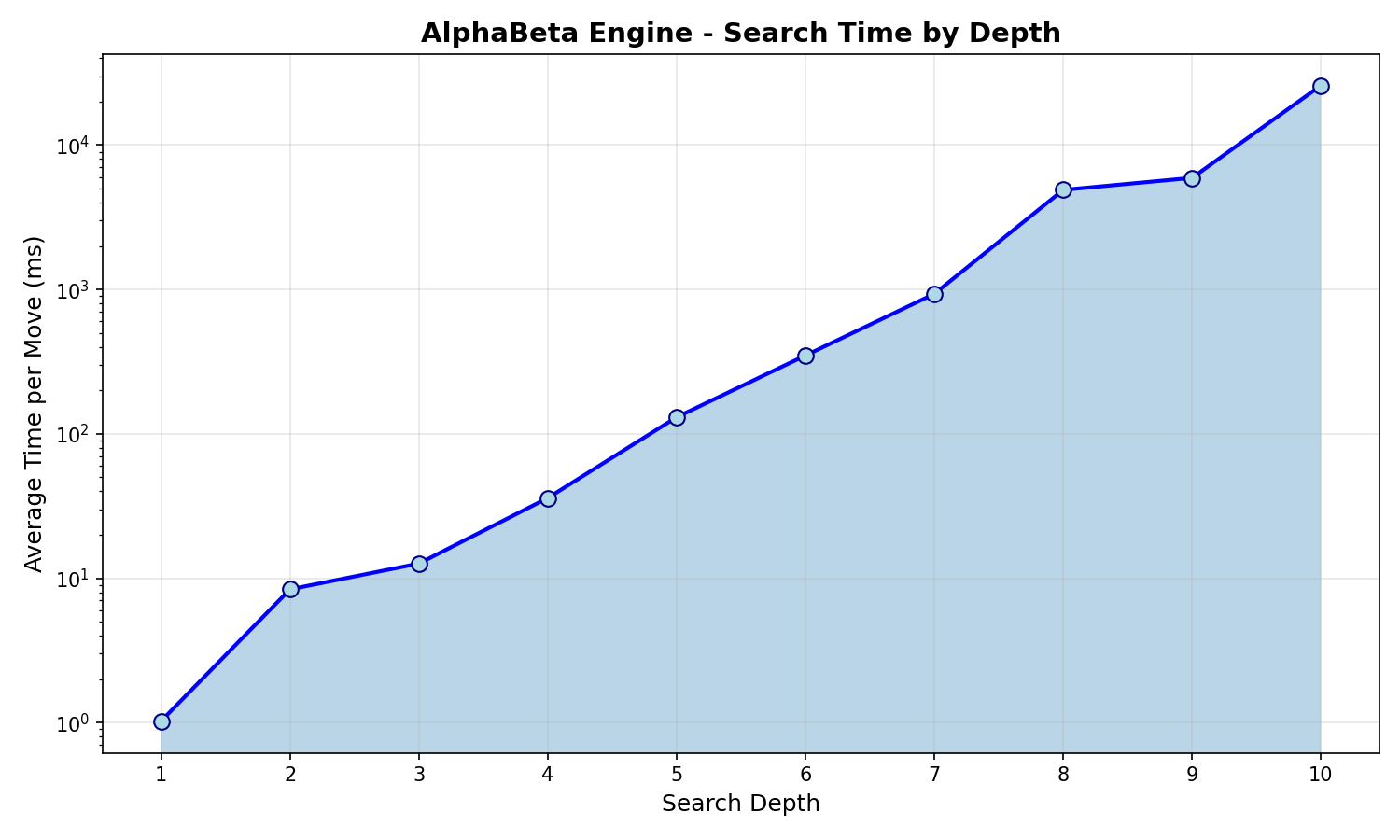
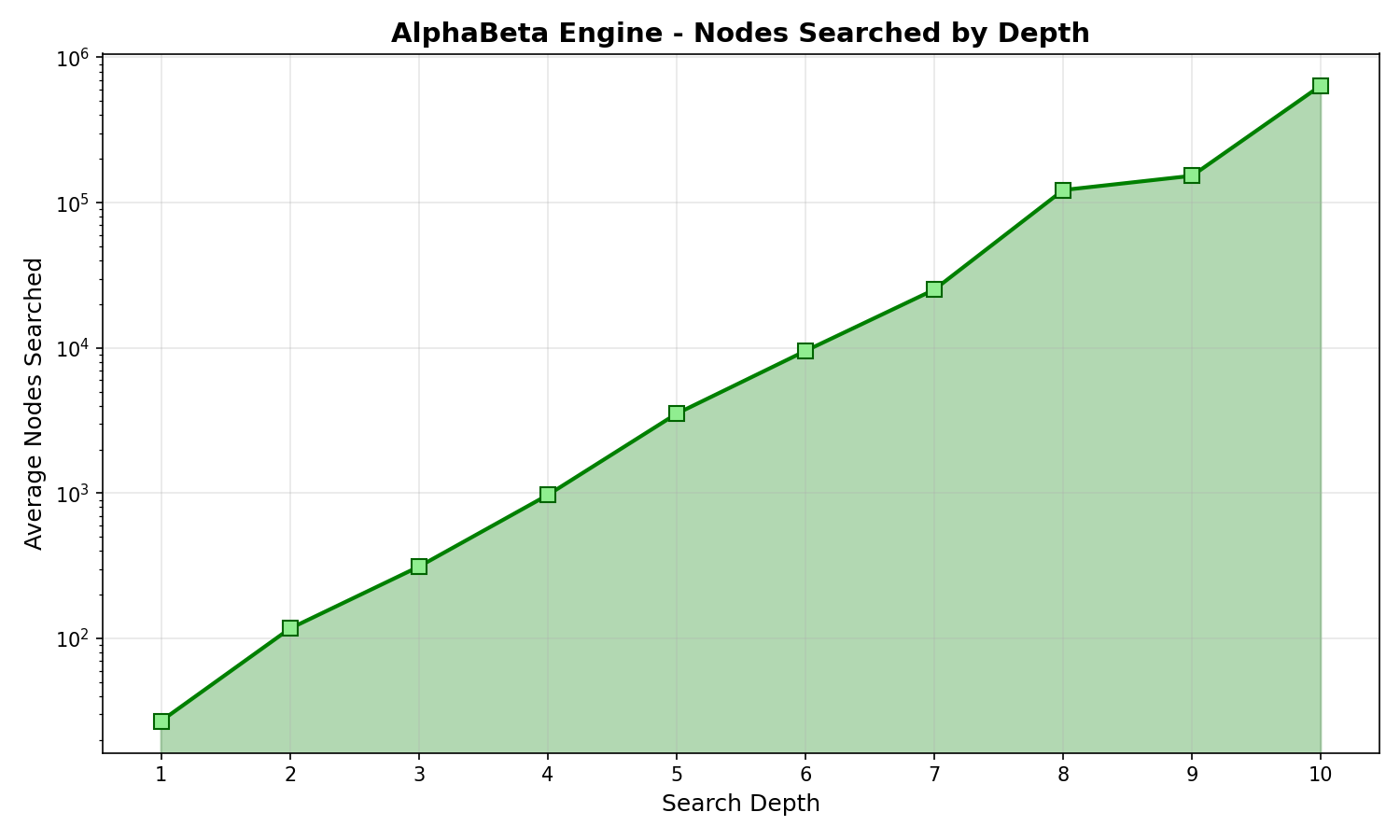
Engine Depth Performance
AlphaBeta engine search performance at different depths:
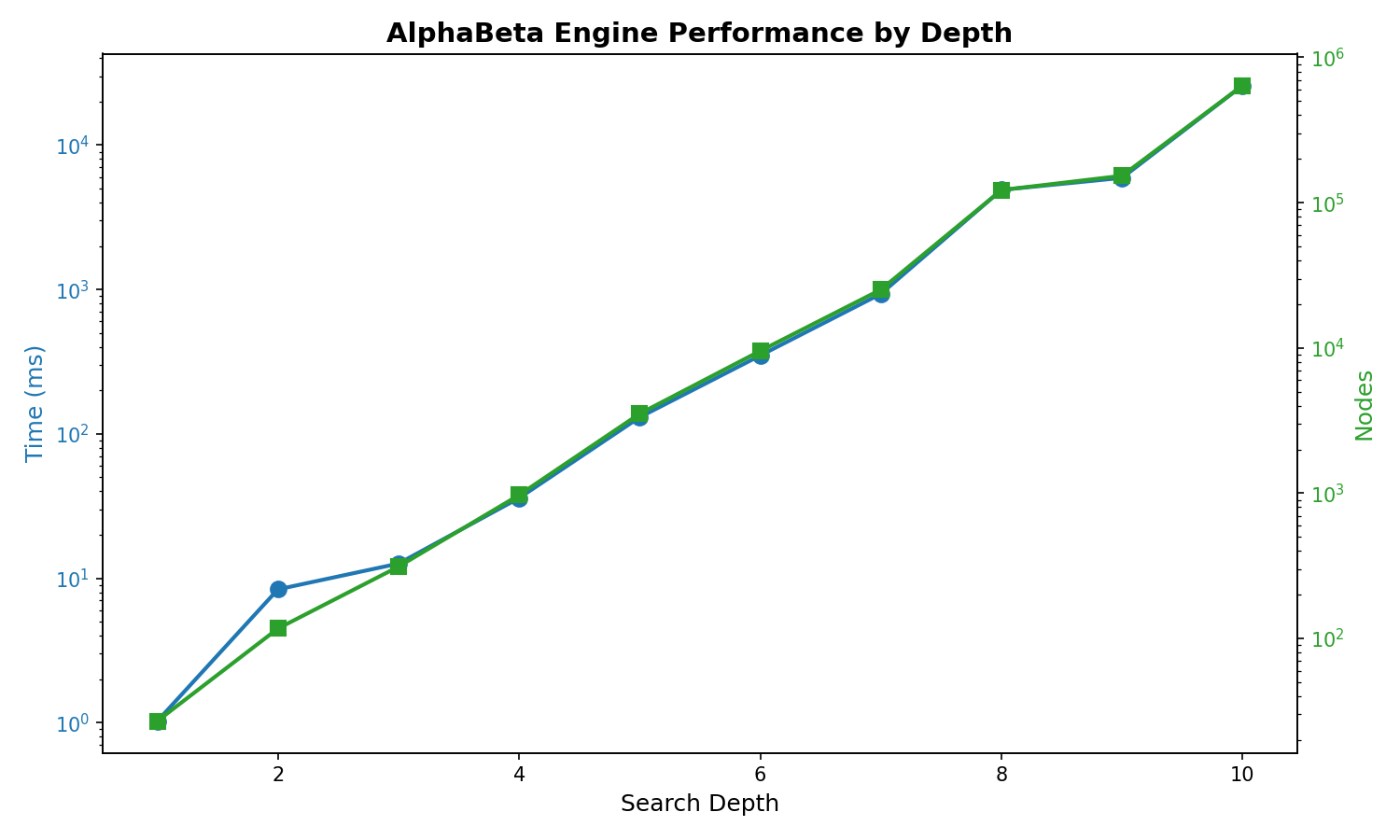
Depth |
Avg Time |
Avg Nodes |
|---|---|---|
1 |
1.03 ms |
27 |
2 |
8.37 ms |
117 |
3 |
12.64 ms |
312 |
4 |
35.92 ms |
971 |
5 |
130.32 ms |
3,525 |
6 |
349.03 ms |
9,537 |
7 |
932.85 ms |
25,202 |
8 |
4.90 s |
122,168 |
9 |
5.93 s |
153,152 |
10 |
25.90 s |
641,085 |
Overview
The benchmarking system compares performance between different versions of py-draughts by:
Creating snapshots (wheel files) of the current version
Running benchmarks comparing a snapshot against the current source code
Workflow
Create a Snapshot
First, create a snapshot of the version you want to use as baseline:
python tools/create_snapshot.pyThis will:
Build a wheel file from the current source
Save it to
snapshots/snapshot_YYYYMMDD_HHMMSS/Store metadata (git commit, timestamp) in
metadata.json
Compare Versions
Then compare the snapshot against your current (modified) source:
# Compare latest snapshot vs current source python tools/compare_versions.py # Compare specific snapshot vs current source python tools/compare_versions.py snapshots/snapshot_20251231_125057
The comparison runs:
Legal moves benchmark: Measures time to generate legal moves from various positions
Engine match: Plays games between engines to compare move quality and speed
Configuration
The benchmark configuration is defined at the top of tools/compare_versions.py:
WARMUP_ROUNDS = 5
BENCHMARK_ROUNDS = 10
BENCHMARK_ITERATIONS = 10
ENGINE_DEPTH = 2
NUM_GAMES = 20
Results
Benchmark results are automatically appended to benchmark_results.csv in the project root.
Optimization Workflow
Recommended workflow for improving engine performance:
Profile
Run profiling to identify bottlenecks:
# For general engine profiling python tools/profile_engine_detailed.py # For legal moves generation specifically python tools/profile_legal_moves.py
Improve
Make code changes to address identified bottlenecks.
Verify Profile
Run the profiling script again to verify local improvements.
Test
Ensure no regressions in functionality:
pytest .Benchmark
Compare against the baseline snapshot to verify performance gains:
python tools/compare_versions.pySnapshot
If satisfied with the results, create a new snapshot to serve as the next baseline:
python tools/create_snapshot.py
Profiling
For detailed profiling of specific functions, use:
python tools/profile_engine.py
Or for more detailed analysis:
python tools/profile_engine_detailed.py 5 # depth 5
This uses Python’s cProfile to identify bottlenecks in the engine.
Generating Benchmark Charts
To regenerate the benchmark charts and tables for documentation:
python tools/generate_benchmark_charts.py
This will:
Run legal moves generation benchmarks across various position types
Run engine depth benchmarks from depth 1 to 10
Generate PNG charts in
docs/source/_static/Output RST table content for copying into documentation
The generated charts include:
legal_moves_benchmark.png- Bar chart of legal moves generation time by position typeengine_benchmark.png- Combined time and nodes chart for engine depthsengine_depth_time.png- Logarithmic time chart by depthengine_depth_nodes.png- Logarithmic nodes searched chart by depth